Know more your ignition engine system, read this ignition component first (part 1)
Ignition System Components
A. Battery
This
component serves to provide current 12 Volt low voltage for the ignition coil.
The battery is an electrochemical made to supply power to the engine starter
system, ignition system, lights, and other components. This tool store
electrical energy in the form of chemical energy released when needed and
supply it to each of the electrical system. The charging cycle and expenditures
occur continuously.
1.
Battery
Construction
In
the sulphuric acid electrolyte batteries are the positive electrode and negative
electrode in the form of plates. The rooms are divided into several cells, and
in each - each cell there are some elements that are submerged in the
electrolyte.
a. Battery element
Inter
plates positive and negative each connected by a strap plate. Bond positive and
negative plates mounted alternately bounded by separator and fiberglass, the
preparation of this plate broad aim enlarge allusion between the active
ingredient and the electrolyte so that the electricity generated great.
b. Electrolyte
Battery
electrolyte is a sulphuric acid solution with distilled water, the density of
the electrolyte in the battery in a fully charged state is 1,260 or 1,280 (at a
temperature of 20º C). 1.260 specific gravity electrolyte containing 65%
distilled water and 35% sulphuric acid, while the electrolyte density 1.280
containing 63% water and 37% sulphuric acid.
c. Battery box
Battery
boxes are divided into six rooms or cells, in which there is a sign of upper
and lower surfaces. Elevated position from the base plate and given a baffle,
aim to prevent the short circuit.
d. Ventilation Stoppers
Stoppers
vent is close to filling hole electrolytes, aims to separate hydrogen gas out
through the ventilation holes while the sulphuric acid vapour condenses on the
edge of the vent and drip back down.
B. Ignition Switch
The ignition system ignition serves to
connect and disconnect the electric current flow from the battery to the
ignition coil.
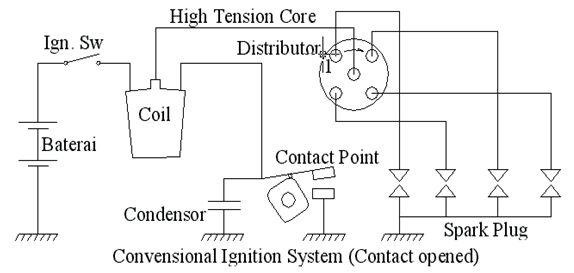
C. Ignition Coil
In this system, the ignition coil
serves to raise the voltage (12 V) into a high-voltage (15 KV to 20 KV)
required for ignition. To enhance the low voltage of the ignition coil there
are two coils, namely;
1. Primary coils. This coil creates a
magnetic field serves the ignition coil to be raised on the coil-coil
induction. Characteristic of the primary coil is a coil that has a large cross
section and roll a little.
2. Secondary coil. This coil serves to add
an induction into a high voltage to the spark plugs were subsequently channelled
into a spark. The hallmark of the secondary coil is a coil that has a small
cross section and rolls very much. For more details, see the image below.
a.
The
workings of the ignition coil
The theory of the high voltage
The
voltage that occurs in the coil ignition coil based on the principle of mutual
induction / induction together. If on an iron bar wrapped so that it becomes a
fine wire coil, then electrified, then in the iron core magnetism will occur
with the line style.
A
magnetic force that occurs in the iron core depends on two factors, there are;
a large number of coil windings and the current flowing in the coil
if
the contact point is open, an electric current flowing from the battery to be
disconnected, but the lines of magnetic force that arises in the iron core
tends to continue the flow of electric current. The tendency lines of magnetic
force to continue the flow of electric current will cause an electric current
to the coil even if the electric current of the battery is not flowing. This
incident is said to coil induced by lines of magnetic force are lost because
only the induced coil is called induction alone
b.
Various
Ignition Coil.
On vehicles
generally use three kinds of ignition coil;
1) Canister Type
This type has an iron core in the
middle and the secondary coil surrounds the iron core. The primary coil is
located on the outer side of the secondary coil. Overall components are
assembled in a house in a metal canister. Sometimes a canister filled with oil
(lubricant) to help reduce the heat produced by the coil. Constructions type of
canister as shown in the figure below.
2) Moulded
Moulded-type coil is a type that is
now commonly used. In this type of iron core in the middle, surrounded by the
primary coil, while the secondary coil is located on the outside. Overall
assembled components are then wrapped in resin (amber) to be resistant to
vibration commonly found in motorcycles.
Moulded type of coil a popular
choice because it is resistant and robust construction. In multicylinder
engines (many cylinder) usually one coil serves two spark plugs because it has
two high voltage cables of the secondary coil.
3) The combined coil mode (fused) with cap
plugs (spark plug)
This coil mode is a type of the most
recent and often referred to as coil rod (stick coil). The large size and
weighs less than the type of moulded coil and biggest advantage is this coil
does not require a high voltage cable.










Comments
Post a Comment